
Introduction
Fedora 40 is the latest iteration of the popular Fedora Linux distribution, known for its cutting-edge features and commitment to open-source principles. This release focuses on enhancing the desktop environment, making it more user-friendly, efficient, and visually appealing. In this content, we will explore the Fedora 40 Desktop Environment using the 5W1H approach (What, Who, Where, When, Why, How), along with the consequences and conclusion of these improvements.
Overview
What
Fedora 40 offers a robust desktop environment that includes the latest GNOME desktop, improved system performance, and enhanced security features.
Who
Fedora 40 is developed and maintained by the Fedora Project, which is sponsored by Red Hat. It is intended for developers, system administrators, and desktop users who prefer cutting-edge open-source technology.
Where
Fedora 40 can be downloaded from the official Fedora Project website. It is available for multiple architectures including x86_64 and ARM.
When
Fedora 40 was released in October 2024, following the Fedora Project's regular six-month release cycle.
Why
Fedora 40 introduces several new features and improvements that aim to enhance the overall user experience and system performance.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Cutting-edge software | May have stability issues |
| Improved security features | Steep learning curve for new users |
| Strong community support | Limited support for older hardware |
How
Follow these steps to install Docker on Debian 12 Bookworm:
| Step 1 | Fedora 40 can be installed by downloading the ISO file from the Fedora Project website. |
| Step 2 | creating a bootable USB drive. |
| Step 3 | and following the installation instructions. |
Consequences
| Positive |
|
| Negative |
|
Conclusion
Fedora 40 represents a significant step forward in desktop environments, combining cutting-edge features with strong security. While it may present a learning curve for new users, its benefits make it a valuable tool for developers and advanced users.
GNOME Desktop
If you installed Fedora without GUI but now need GUI because of GUI required applications and so on, Install Desktop Environment like follows.
Step [1]Install GNOME Desktop Environment on this example.
[root@bizantum ~]# dnf -y group install "Basic Desktop" GNOME
Step [2] After installing Desktop, to start Desktop session on CUI, re-login with a common user and run like follows.
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ echo "/usr/bin/gnome-session" >> ~/.xinitrc
# for the case to use classic mode
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ echo "env GNOME_SHELL_SESSION_MODE=classic /usr/bin/gnome-session" >> ~/.xinitrc
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ startx
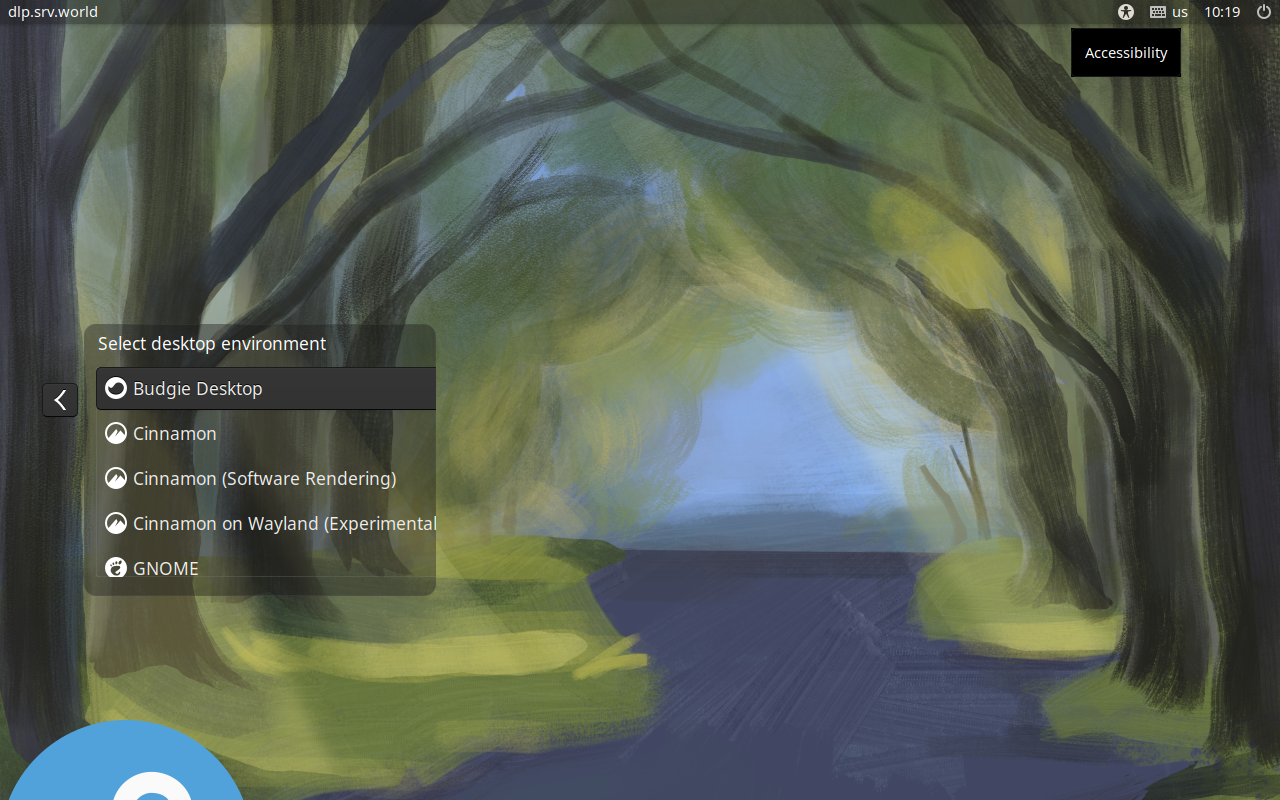
Step [3]If you would like to change your System to Graphical Login as default, Change setting like here and restart computer. Then, Graphical Login screen is shown like follows.
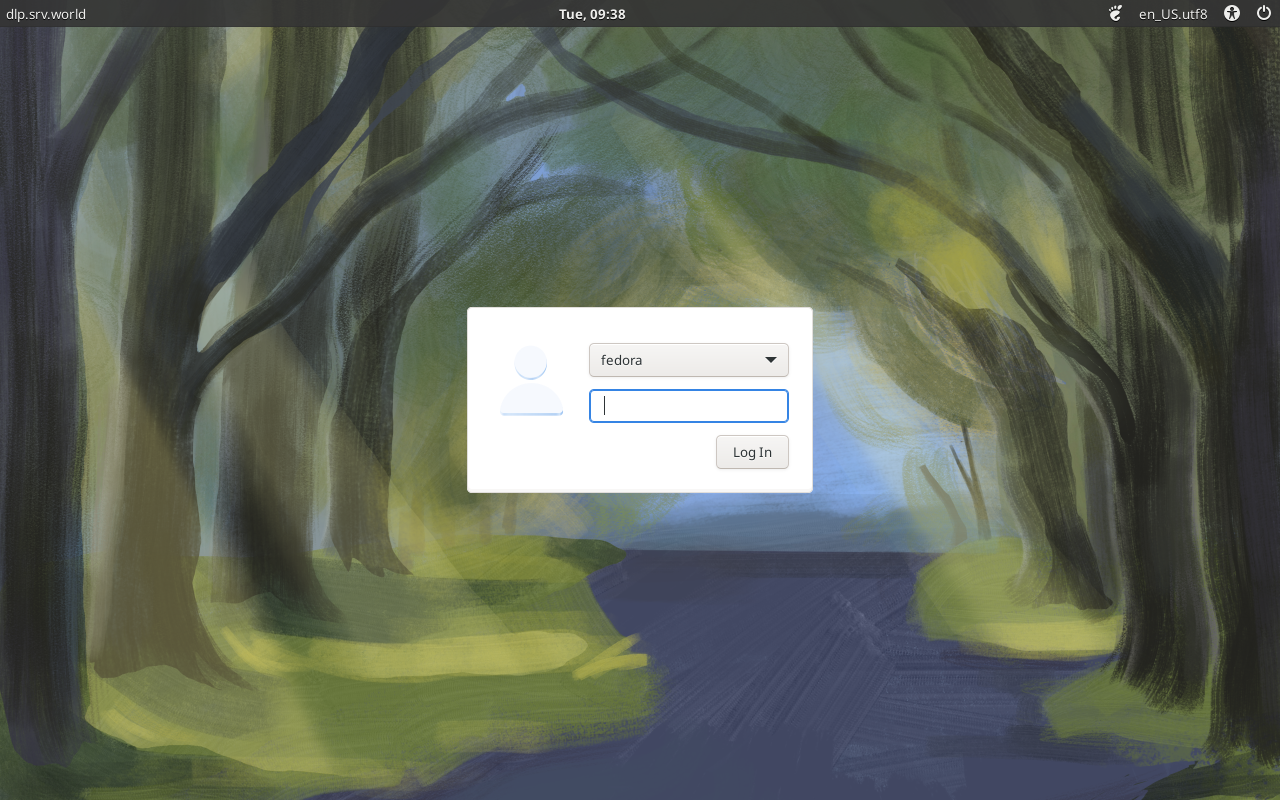
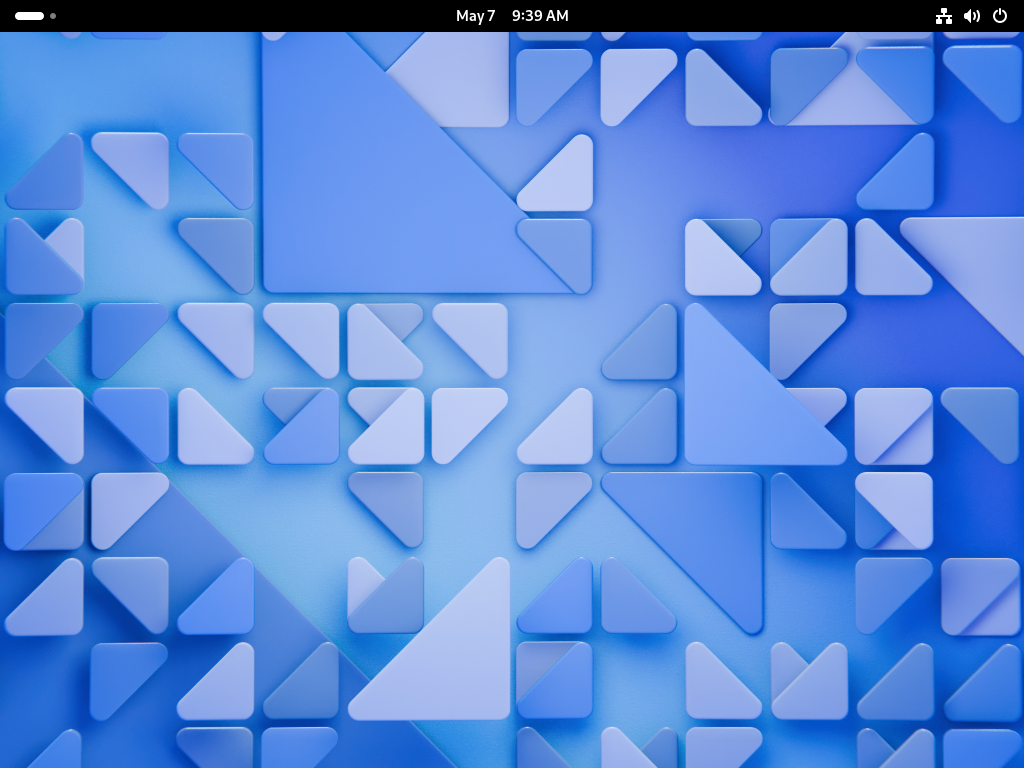
Step [4] When initial login for each user, they should select language or keyboard settings. After configuring initial login settings, GNOME Desktop session starts like follows.
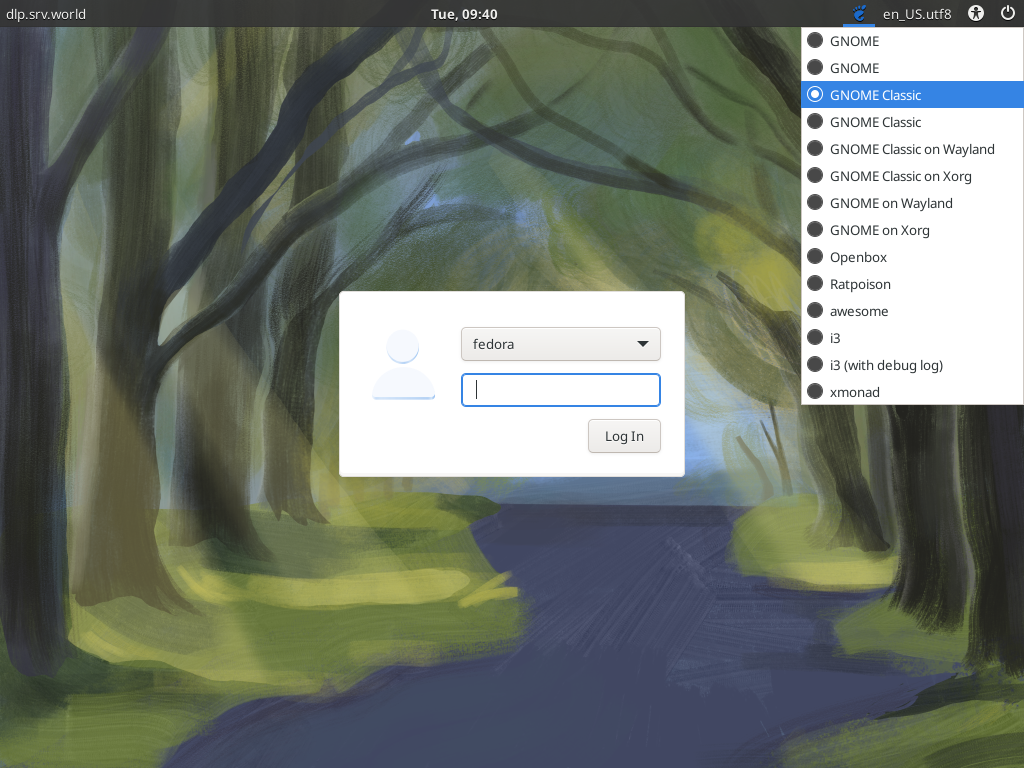
Step [5]GNOME Shell is set default but if you would like to change to Classic mode, then Click the footprints icon that is placed on the upper-right on the login screen and Select [GNOME Classic] on the selection like follows.
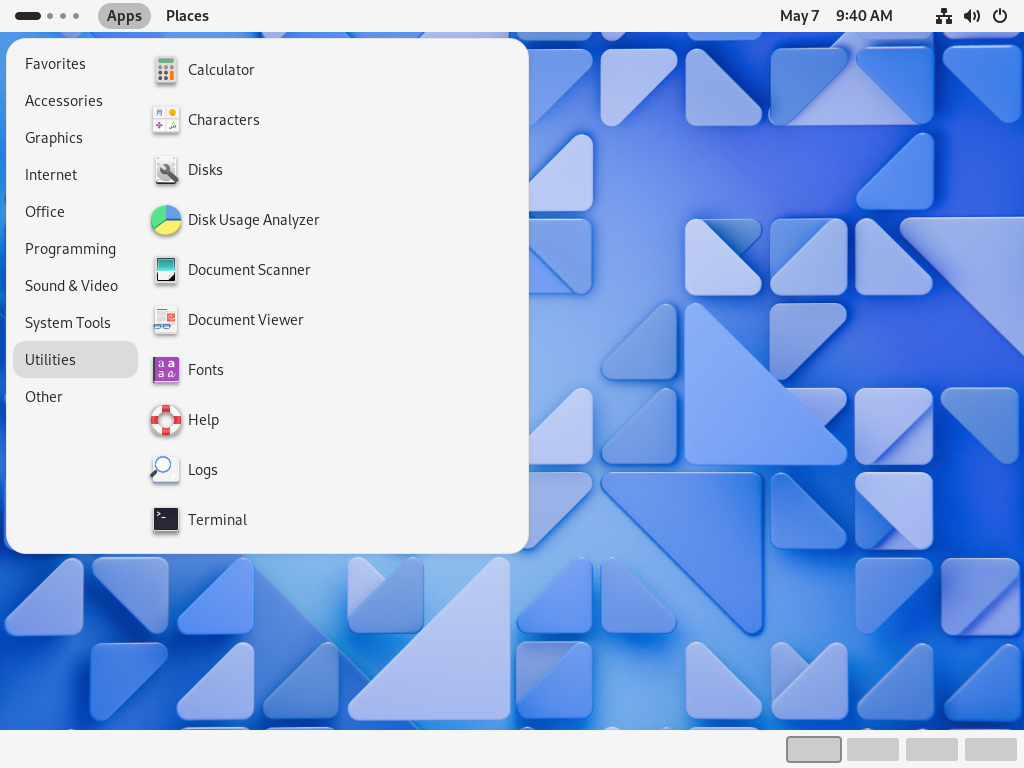
Step [6]GNOME Desktop Classic Session starts.
KDE Desktop
If you installed Fedora without GUI but now need GUI because of GUI required applications and so on, Install Desktop Environment like follows.
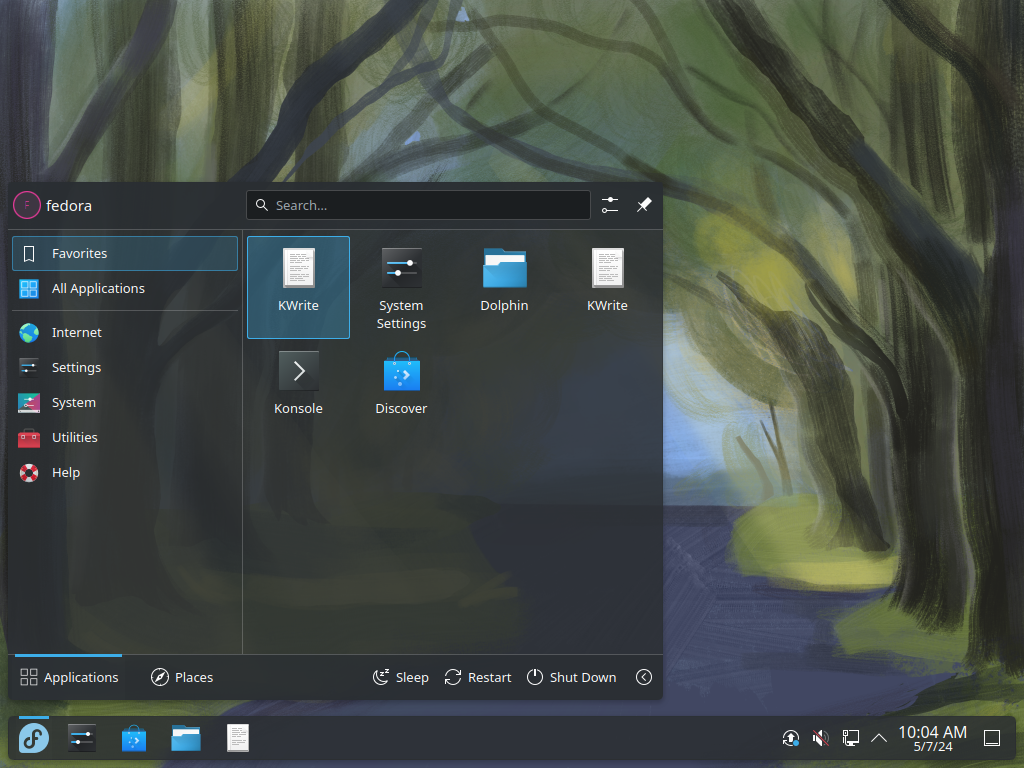
Step [1]Install KDE Desktop Environment on this example.
[root@bizantum ~]# dnf -y group install "KDE Plasma Workspaces"
Step [2]After installing Desktop, to start Desktop session on CUI, re-login with a common user and run like follows.
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ startplasma-wayland
Step [3]If you would like to change your System to Graphical Login as default, Change setting like here and restart computer. Then, Graphical Login screen is shown like follows.
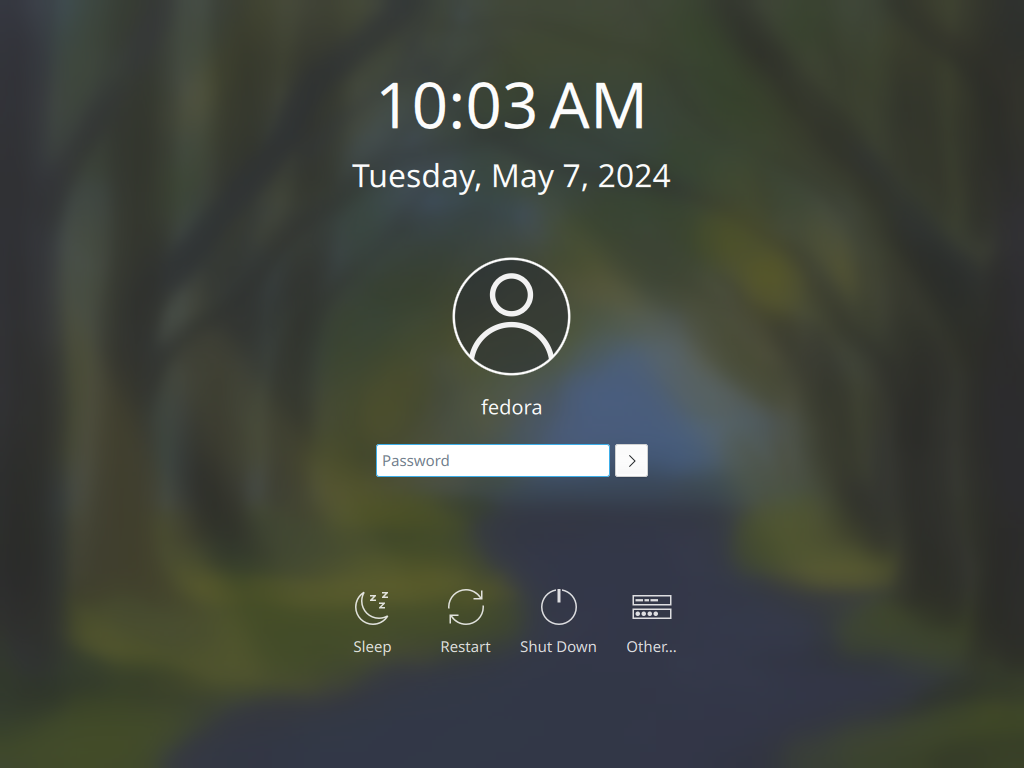
Step [4]KDE Desktop Session starts.
Cinnamon Desktop
If you installed Fedora without GUI but now need GUI because of GUI required applications and so on, Install Desktop Environment like follows.
Step [1]Install Cinnamon Desktop Environment on this example.
[root@bizantum ~]# dnf -y group install "Cinnamon Desktop"
Step [2]After installing Desktop, to start Desktop session on CUI, re-login with a common user and run like follows.
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ echo "/usr/bin/cinnamon-session" >> ~/.xinitrc
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ startx
Step [3] If you would like to change your System to Graphical Login as default, Change setting like here and restart computer. After restarting computer, select a user to login, then click the icon on right side and select [Cinnamon] like follows.
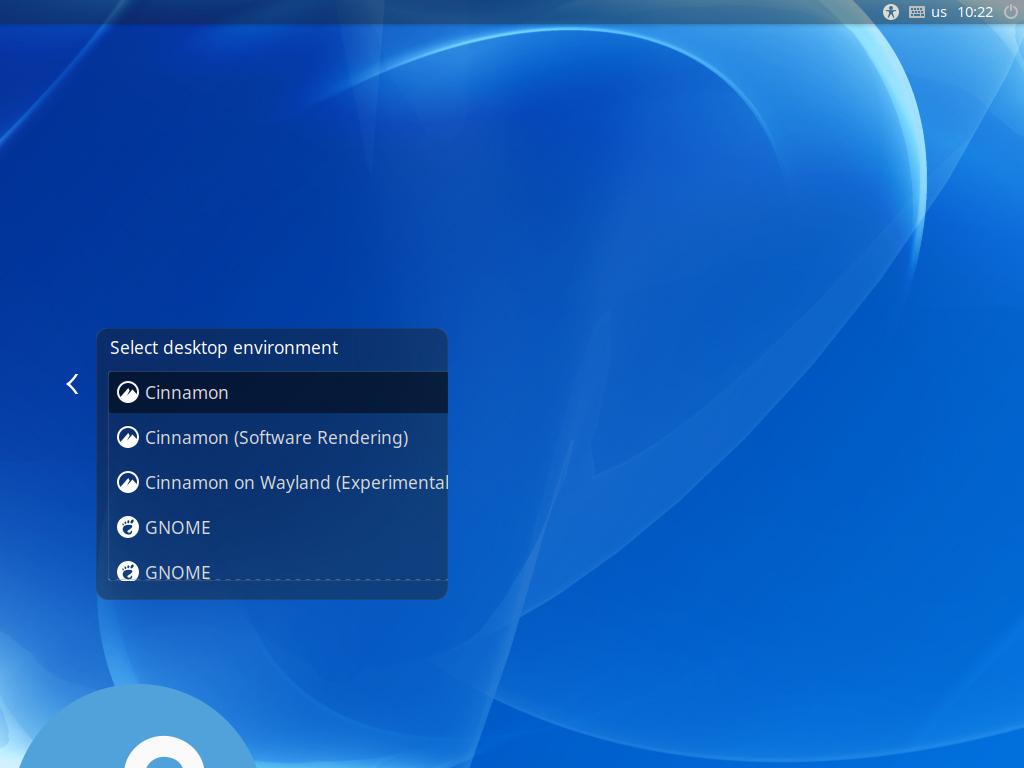
Step [3]Cinnamon Desktop Session starts.
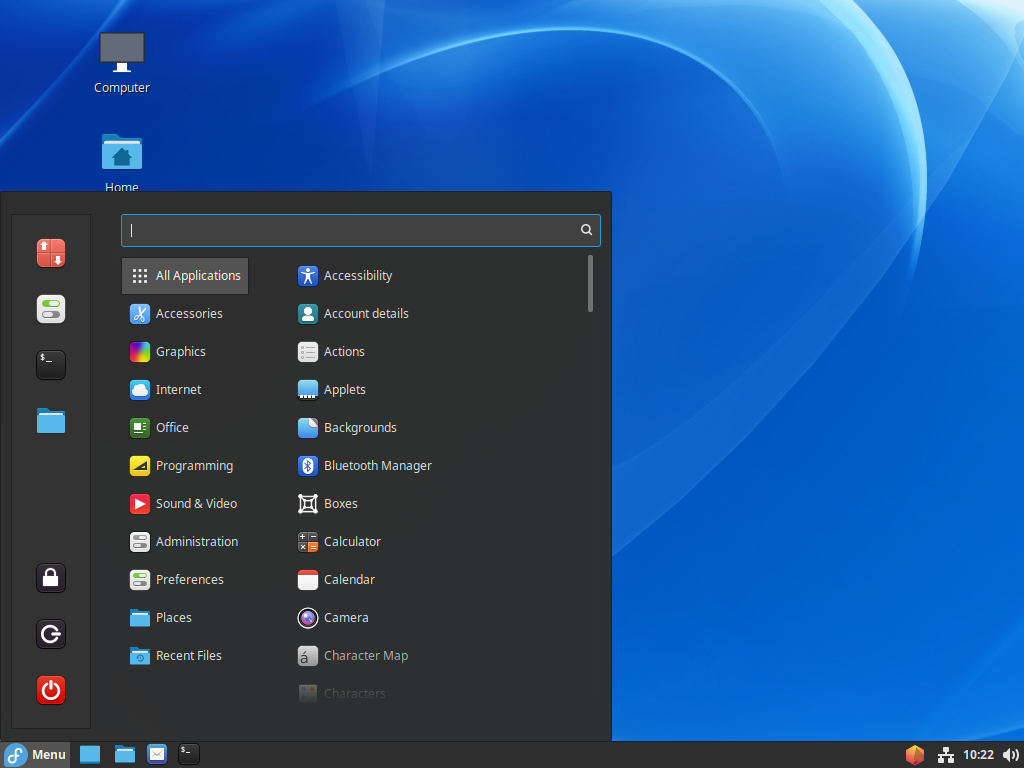
MATE Desktop
If you installed Fedora without GUI but now need GUI because of GUI required applications and so on, Install Desktop Environment like follows.
Step [1]Install MATE Desktop Environment on this example.
[root@bizantum ~]# dnf -y group install "MATE Desktop"
Step [2]After installing Desktop, to start Desktop session on CUI, re-login with a common user and run like follows.
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ echo "/usr/bin/mate-session" >> ~/.xinitrc
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ startx
Step [3] If you would like to change your System to Graphical Login as default, Change setting like here and restart computer. After restarting computer, select a user to login, then click the icon on right side and select [MATE] like follows.
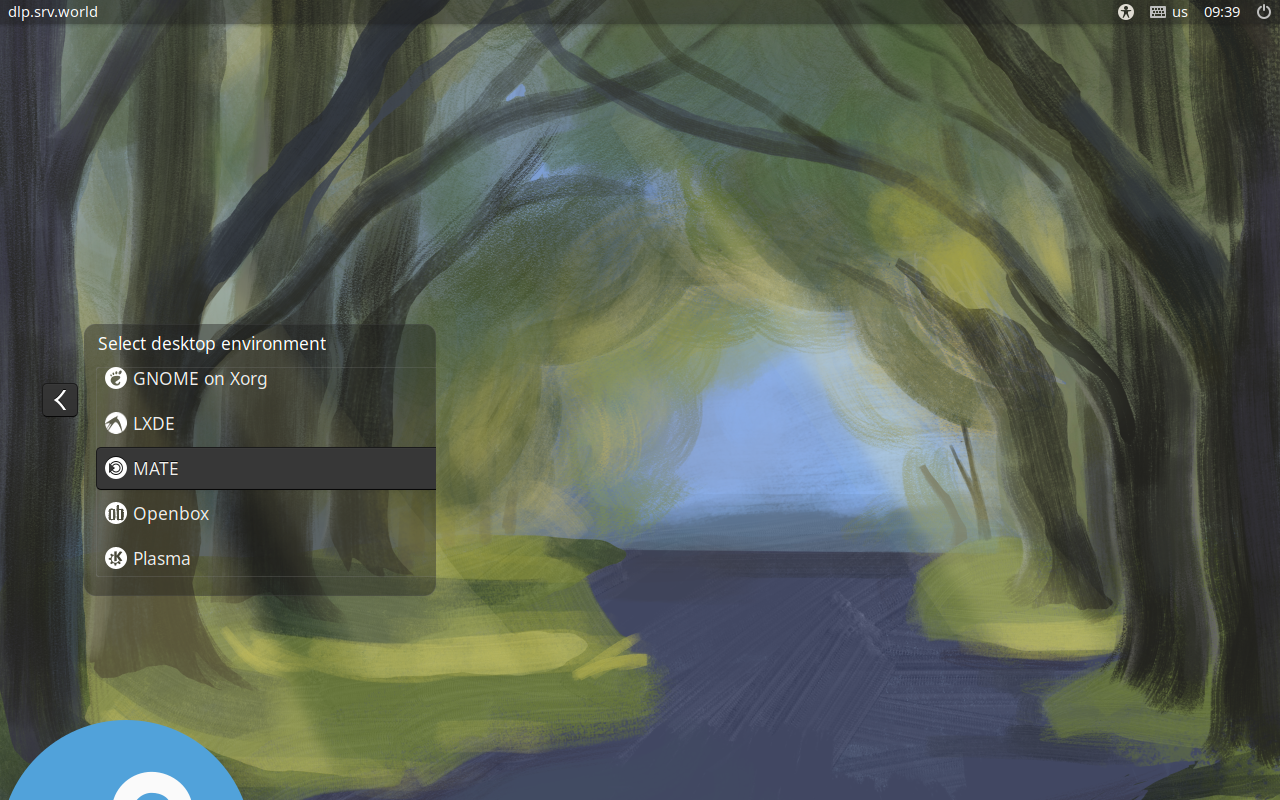

Step [4]MATE Desktop Session starts.
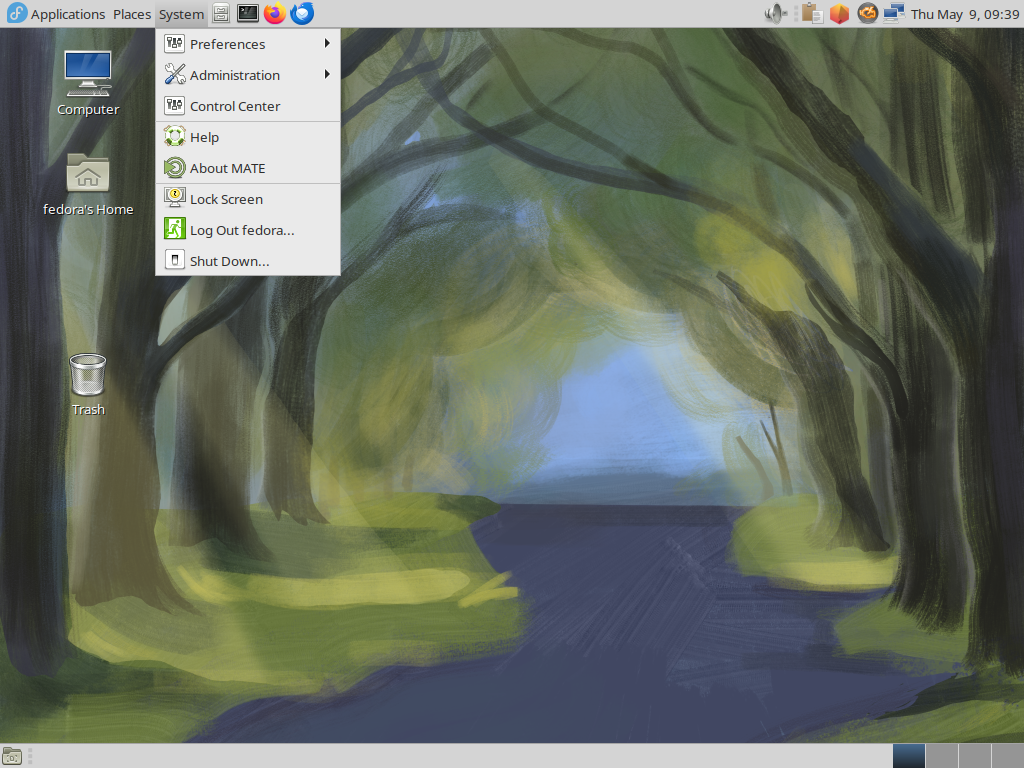
Xfce Desktop
If you installed Fedora without GUI but now need GUI because of GUI required applications and so on, Install Desktop Environment like follows.
Step [1]Install Xfce Desktop Environment on this example.
[root@bizantum ~]# dnf -y group install "Xfce Desktop"
Step [2]After installing Desktop, to start Desktop session on CUI, re-login with a common user and run like follows.
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ echo "/usr/bin/startxfce4" >> ~/.xinitrc
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ startx
Step [3] If you would like to change your System to Graphical Login as default, Change setting like here and restart computer. Then, Graphical Login screen is shown like follows.
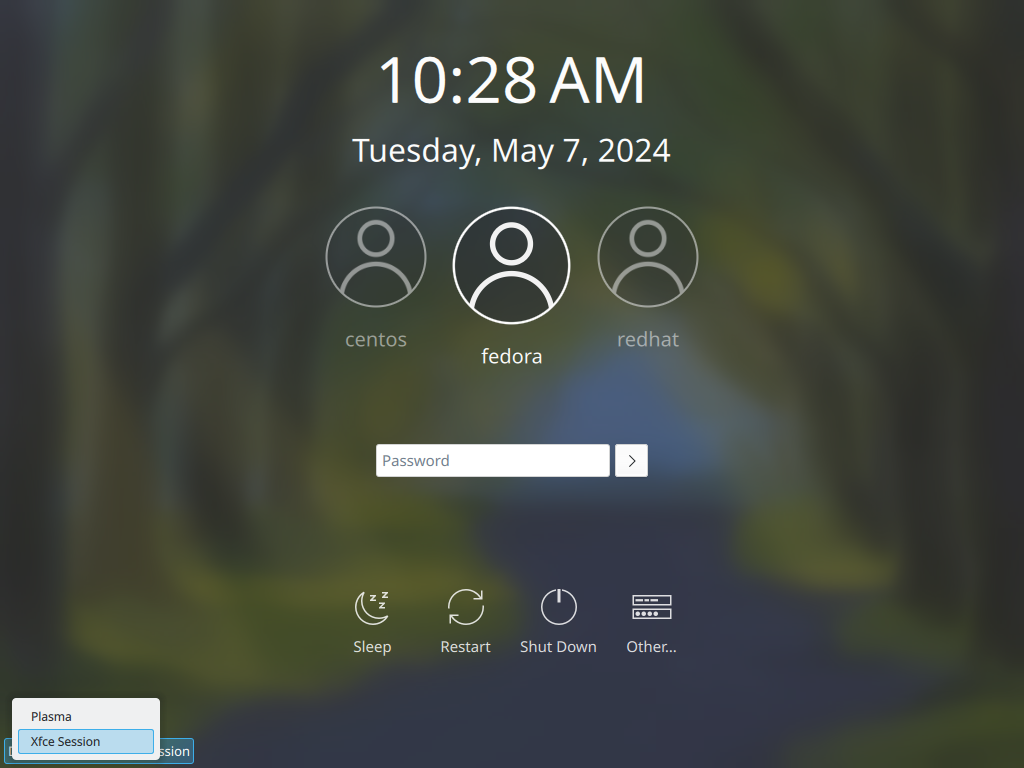
Step [4]Xfce Desktop Session starts.
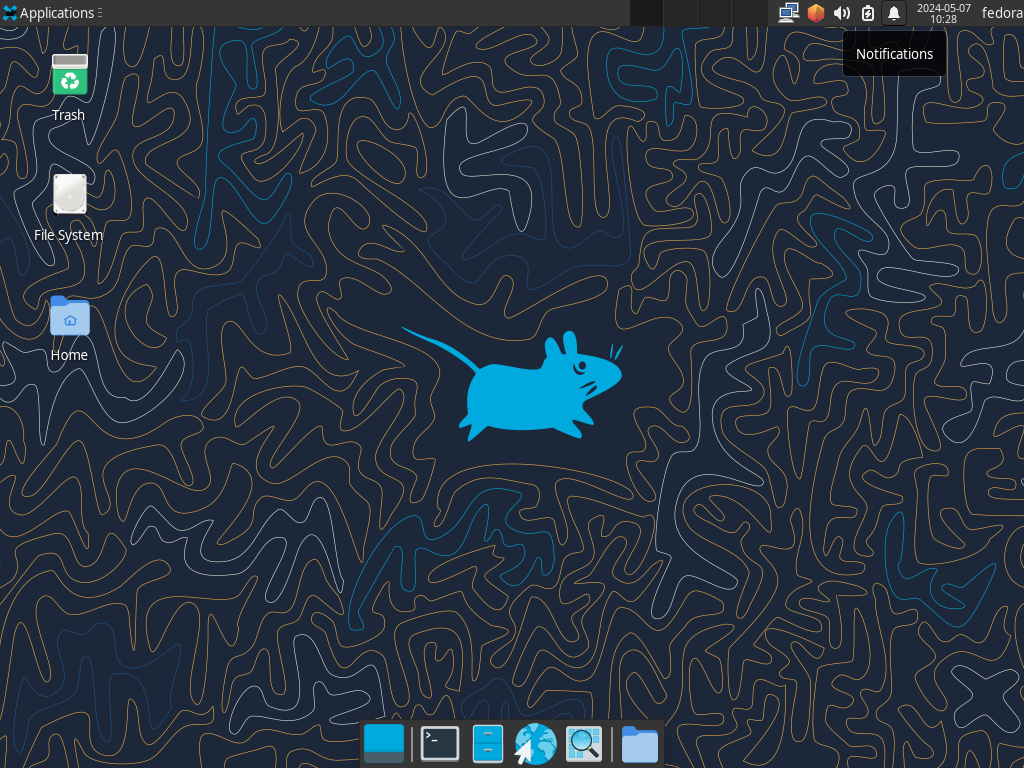
LXDE Desktop
If you installed Fedora without GUI but now need GUI because of GUI required applications and so on, Install Desktop Environment like follows.
Step [1]Install LXDE Desktop Environment on this example.
[root@bizantum ~]# dnf -y group install "LXDE Desktop"
Step [2]After installing Desktop, to start Desktop session on CUI, re-login with a common user and run like follows.
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ echo "/usr/bin/startlxde" >> ~/.xinitrc
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ startx
Step [3] If you would like to change your System to Graphical Login as default, Change setting like here and restart computer. After restarting computer, select a user to login, then click the icon on right side and select [LXDE] like follows.
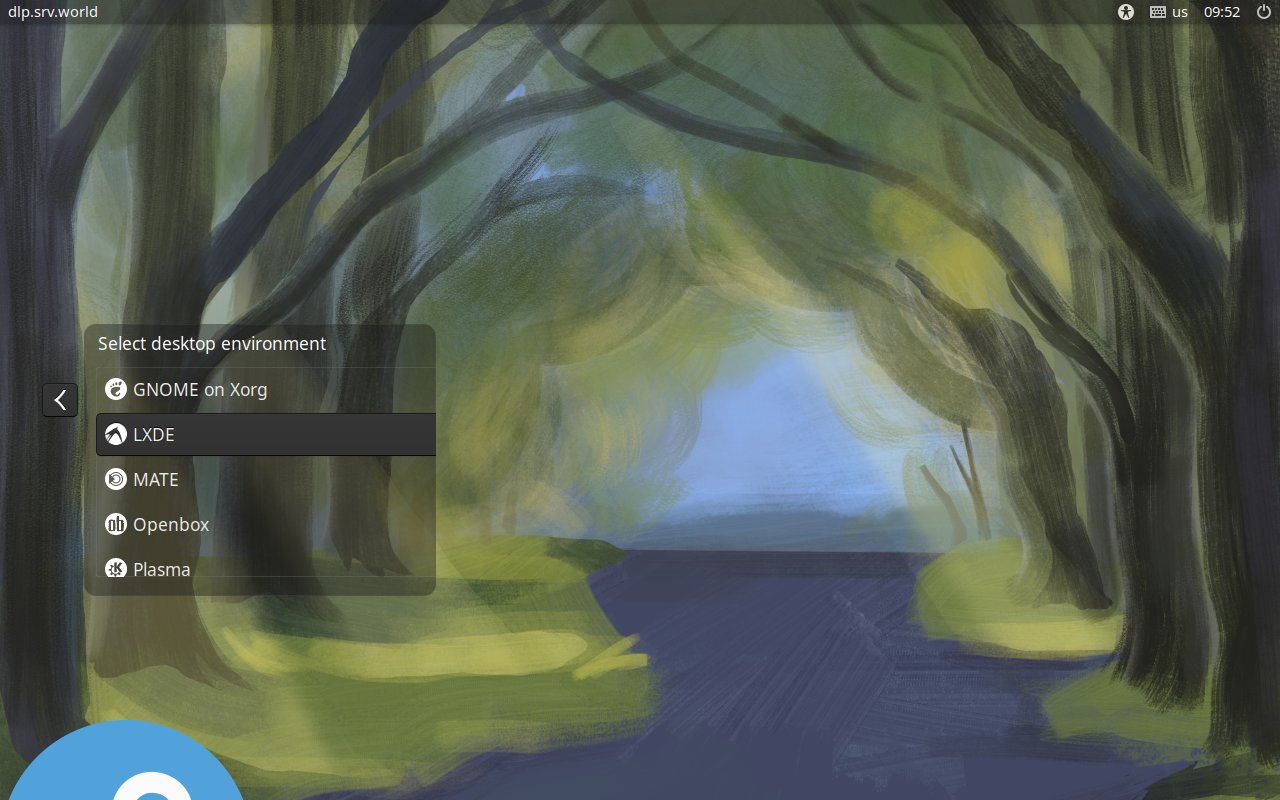

Step [4]LXDE Desktop Session starts.
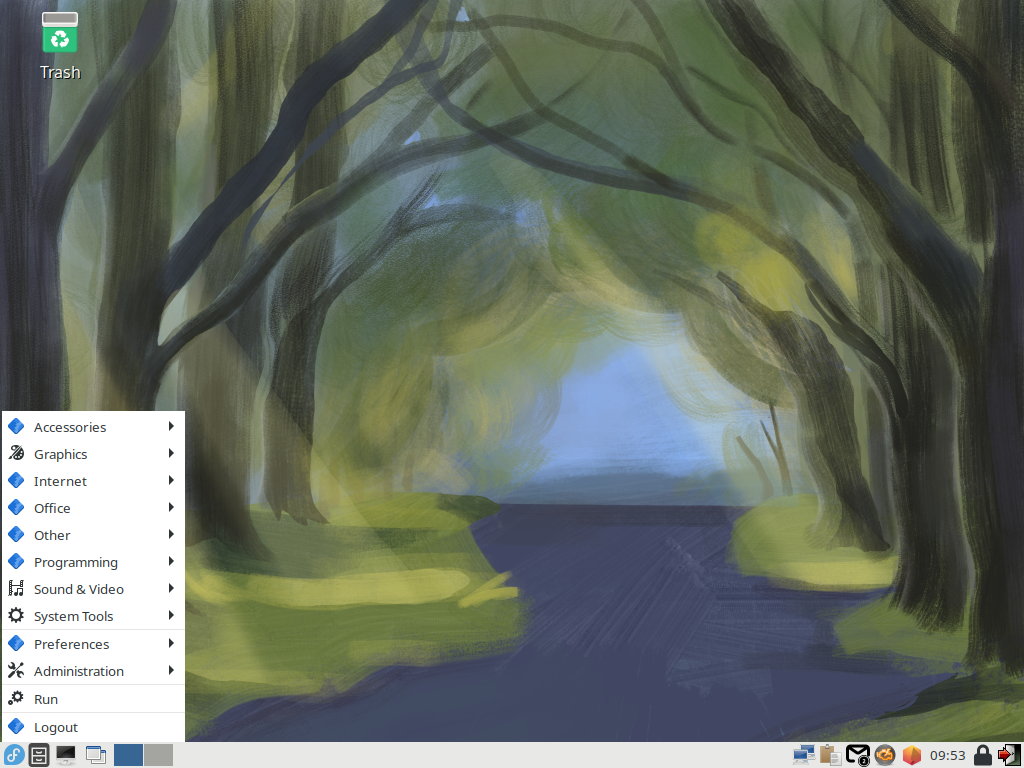
Sugar Desktop
If you installed Fedora without GUI but now need GUI because of GUI required applications and so on, Install Desktop Environment like follows.
Step [1]Install Sugar Desktop Environment on this example.
[root@bizantum ~]# dnf -y group install "Sugar Desktop Environment"
Step [2]After installing Desktop, to start Desktop session on CUI, re-login with a common user and run like follows.
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ echo "/usr/bin/sugar" >> ~/.xinitrc
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ startx
Step [3] If you would like to change your System to Graphical Login as default, Change setting like here and restart computer. After restarting computer, select a user to login, then click the icon on right side and select [Sugar] like follows.
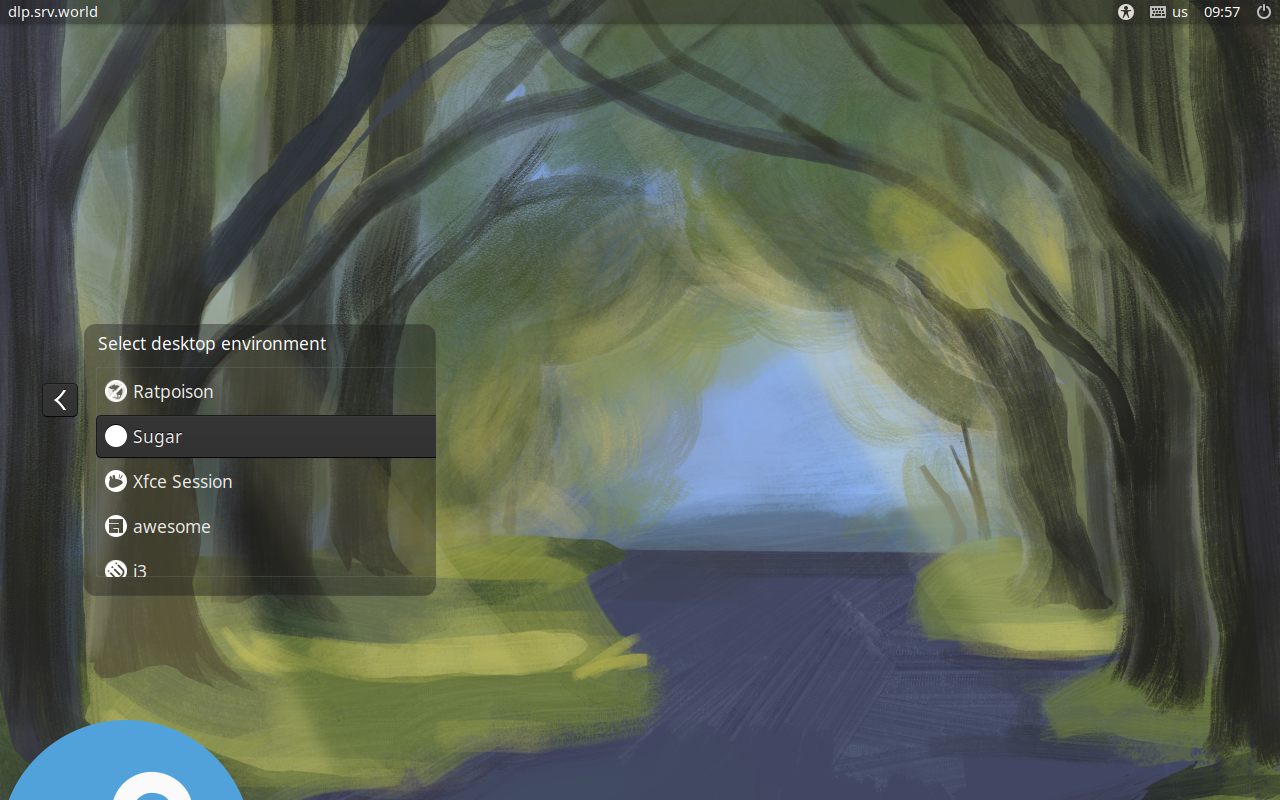

Step [4]Sugar Desktop Session starts.
Budgie Desktop
If you installed Fedora without GUI but now need GUI because of GUI required applications and so on, Install Desktop Environment like follows.
Step [1]Install Budgie Desktop Environment on this example.
[root@bizantum ~]# dnf -y group install "Budgie Desktop"
Step [2]After installing Desktop, to start Desktop session on CUI, re-login with a common user and run like follows.
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ echo "env GNOME_SHELL_SESSION_MODE=Budgie:GNOME /usr/bin/budgie-desktop" >> ~/.xinitrc
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ startx
Step [3] If you would like to change your System to Graphical Login as default, Change setting like here and restart computer. After restarting computer, select a user to login, then click the icon on right side and select [Budgie Desktop] like follows.
Step [4]Budgie Desktop Session starts.
Configure VNC Server
Install VNC Server to connect with GUI from remote client computer.
Step [1]Install VNC Server.
[root@bizantum ~]# dnf -y install tigervnc-server
Step [2]If Firewalld is running, allow VNC service.
[root@bizantum ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=vnc-server
success
[root@bizantum ~]# firewall-cmd --runtime-to-permanent
success
Step [3]Login as a user you would like to configure VNC session.
# set VNC password
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ vncpasswd
Password:
Verify:
Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ vi ~/.vnc/config
# create new
# session=(display manager you use)
# * available sessions are under [/usr/share/xsessions]
# securitytypes=(security options)
# geometry=(screen resolution)
session=gnome
securitytypes=vncauth,tlsvnc
geometry=800x600
Step [4]Configure settings with root privilege and start Systemd Unit.
[root@bizantum ~]# vi /etc/tigervnc/vncserver.users
# add to last line
# specify [:(display number)=(username]
# display number 1 listens port 5901
# display number n + 5900 = listening port
#
# This file assigns users to specific VNC display numbers.
# The syntax is <display>=<username>. E.g.:
#
# :2=andrew
# :3=lisa
:1=fedora
:2=redhat
# start systemd unit
[root@bizantum ~]# systemctl enable --now vncserver@:1 vncserver@:2
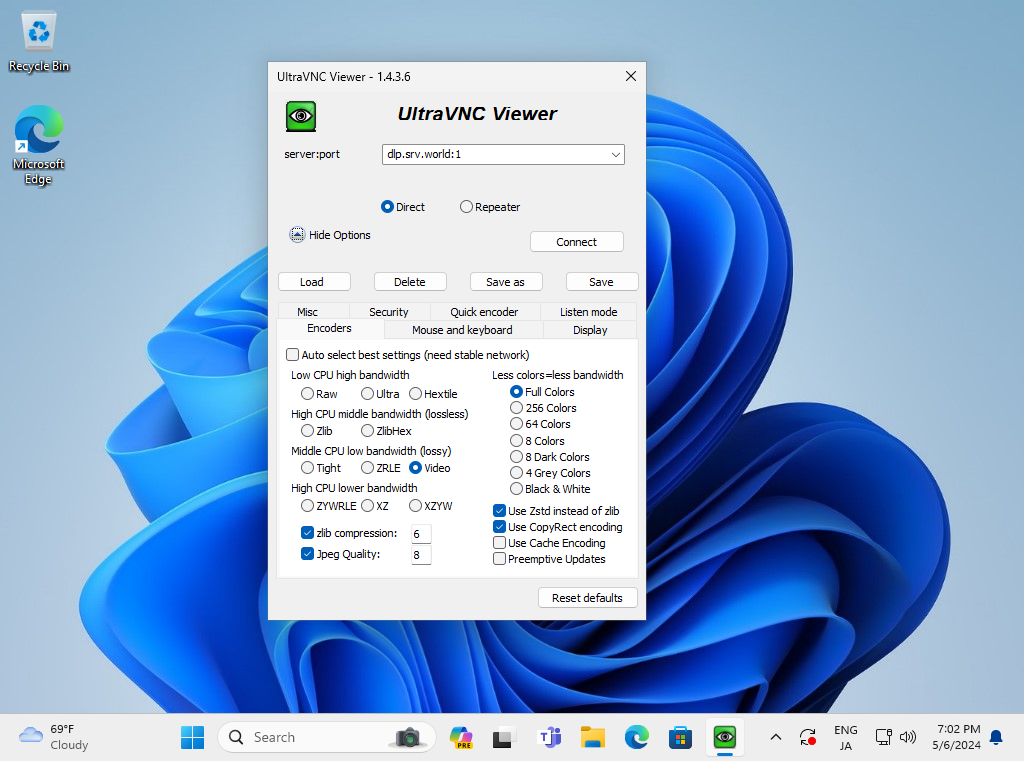
Step [5] Install VNC Viewer on client computer to connect to VNC server. This example is based on Windows 11 and UltraVNC. Download UltraVNC from the site below. ⇒ https://www.uvnc.com/downloads/ultravnc.html After installing UltraVNC, click [UltraVNC Viewer] to run, then, following window is shown. Input [(Server's hostname or IP address):(display number)] like following example and then click the [Connect] button.
Step [6]VNC password is required to input for authentication.
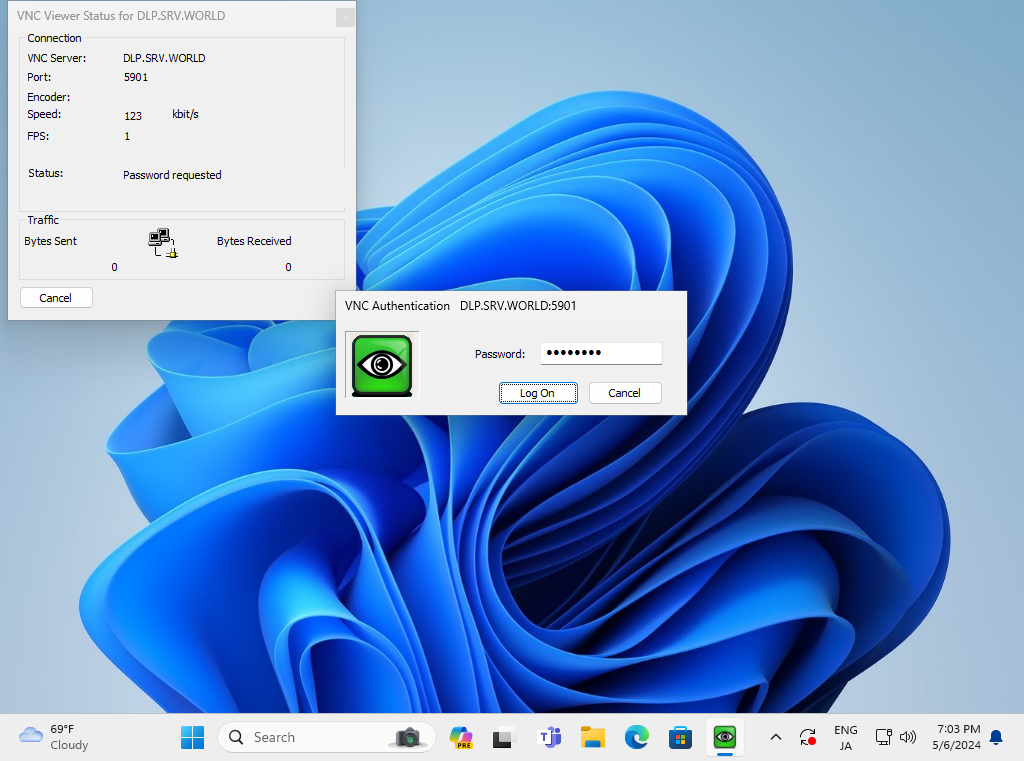
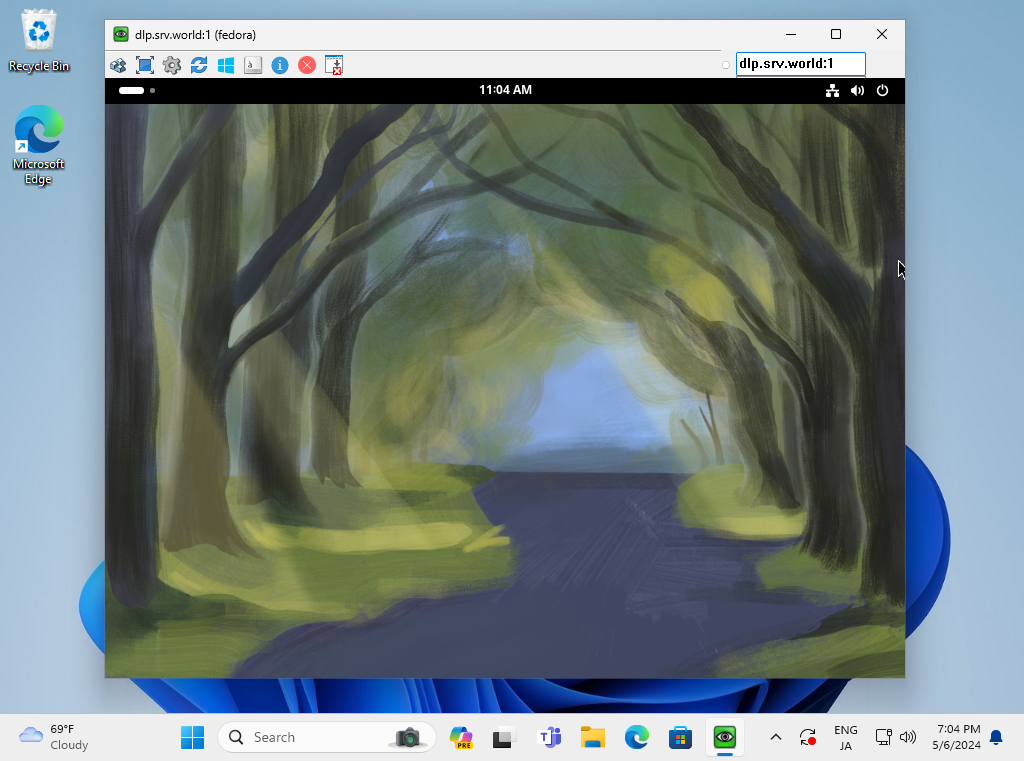
Step [7]If successfully passed authentication, VNC session starts like follows.
Configure Xrdp Server
Install Xrdp Server to connect to Fedora Desktop from the Windows Remote Desktop feature.
Step [1]Install and Start Xrdp Server.
[root@bizantum ~]# dnf -y install xrdp tigervnc-server
[root@bizantum ~]# systemctl enable --now xrdp
Step [2]If Firewalld is running, allow RDP port.
[root@bizantum ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=3389/tcp
success
[root@bizantum ~]# firewall-cmd --runtime-to-permanent
success
Step [3]Login as a user and configure Desktop session on Xrdp.
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ vi ~/startwm.sh
# create new
#!/bin/sh
# GNOME
dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/gnome-session
# GNOME Classic
# env GNOME_SHELL_SESSION_MODE=classic dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/gnome-session
# KDE
# dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/startplasma-wayland
# Cinnamon
# dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/cinnamon-session
# MATE
# dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/mate-session
# Xfce
# dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/startxfce4
# LXDE
# dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/startlxde
# LXQt
# dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/startlxqt
# Budgie
# env GNOME_SHELL_SESSION_MODE=Budgie:GNOME dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/budgie-desktop
# Sugar
# dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/sugar
[fedora@bizantum ~]$ chmod 755 ~/startwm.sh
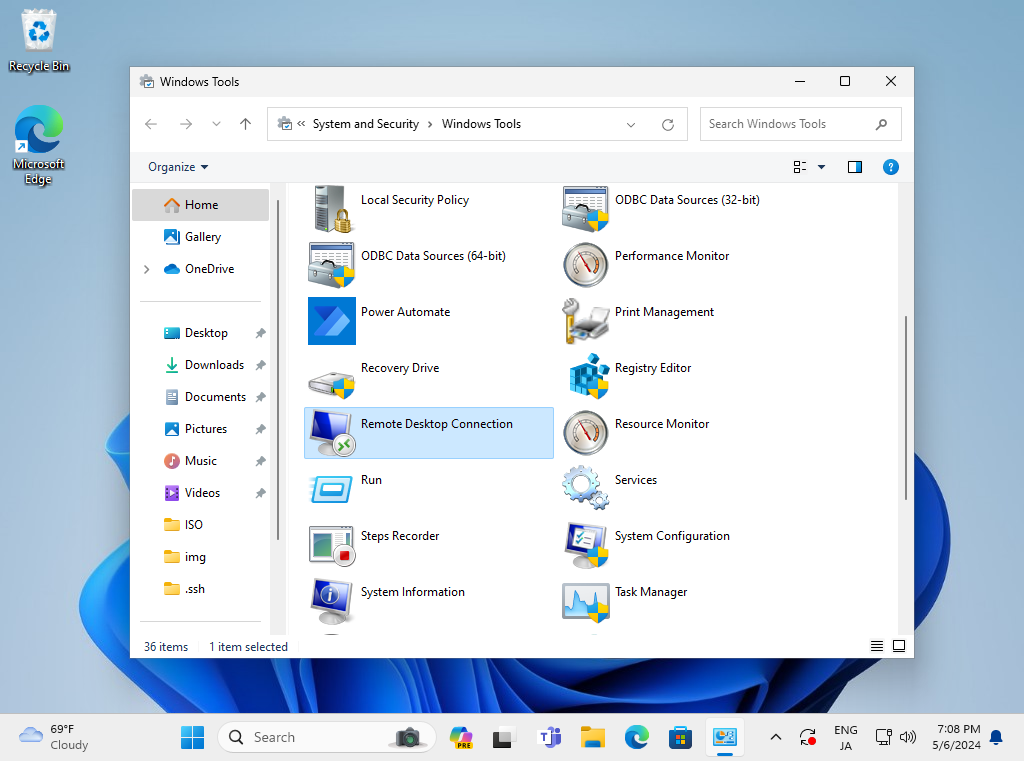
Step [4] Connect from Windows clients. For example on Windows 11. Open Start Menu - [Windows Tool] - [Remote Desktop Connection] to start remote desktop app.
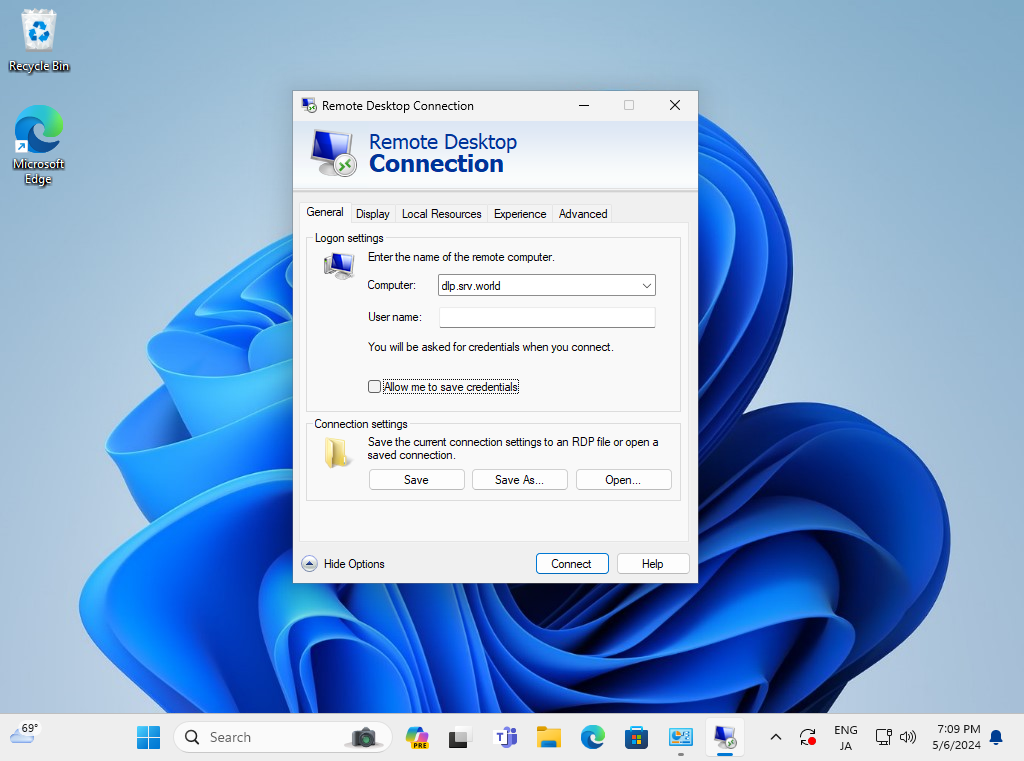
Step [5]Input the hostname or IP address you'd like to connect and push the [Connect] button.
Step [6]Answer with [Yes].
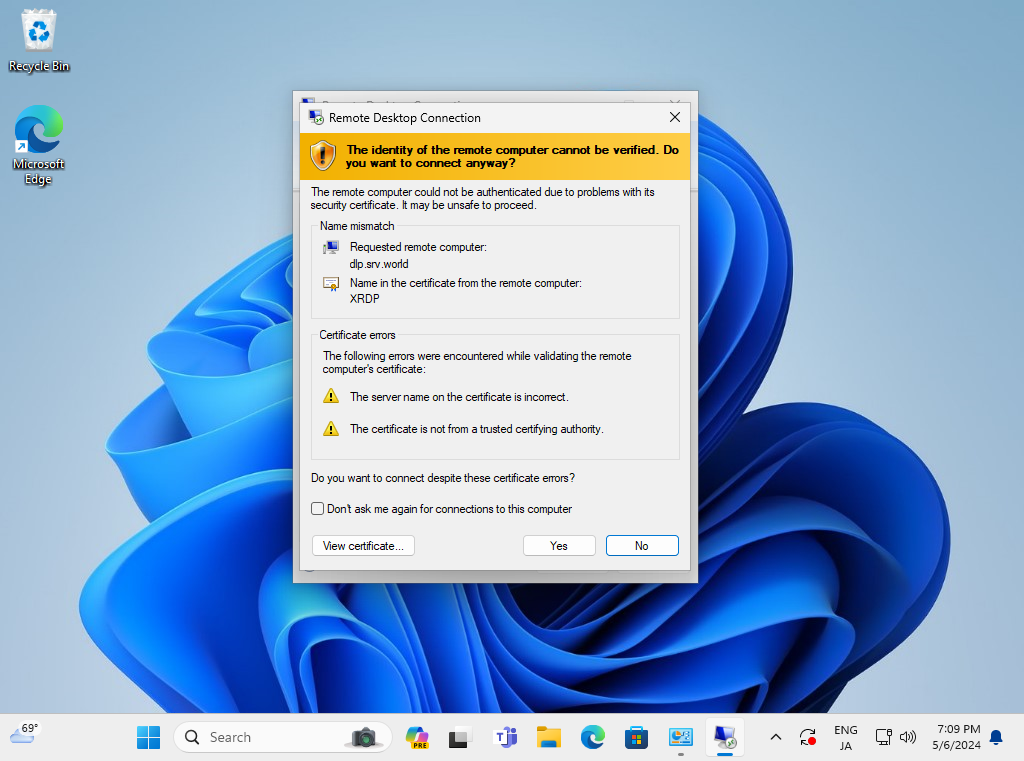
Step [7]Input a user which is on Fedora OS to authenticate.
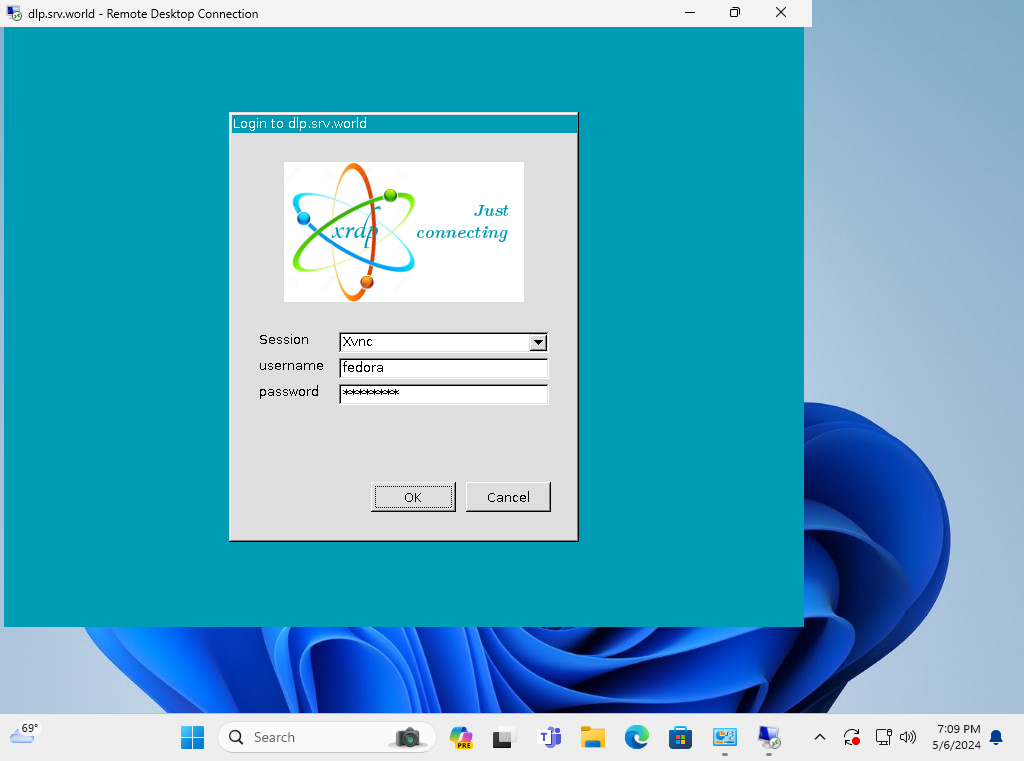
Step [8]If successfully passed authentication, RDP session starts like follows.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps










Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for your comment! We appreciate your feedback, feel free to check out more of our articles.
Best regards, Bizantum Blog Team.