
Initial Settings
Cockpit or Web Admin Console is installed with CentOS Stream 9 Base Environment [Server] or others. It's possible to manage your CentOS Stream server on a Web browser to enable it.
Step [1] On console login prompt, as message is shown like [Activate the web console ***], it's possible to use Admin Console to enable it.
[root@bizantum ~]# systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
[root@bizantum ~]# ss -napt
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:PortProcess
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* users:(("sshd",pid=733,fd=3))
LISTEN 0 4096 *:9090 *:* users:(("systemd",pid=1,fd=46))
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:* users:(("sshd",pid=733,fd=4))
# Cockpit listens 9090 port
# if Firewalld is running, confirm inbound settings (generally cockpit is allowed by default)
[root@bizantum ~]# firewall-cmd --list-service
cockpit dhcpv6-client ssh
# if [cockpit] is not allowed, set it to allow
[root@bizantum ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=cockpit
success
[root@bizantum ~]# firewall-cmd --runtime-to-permanent
success
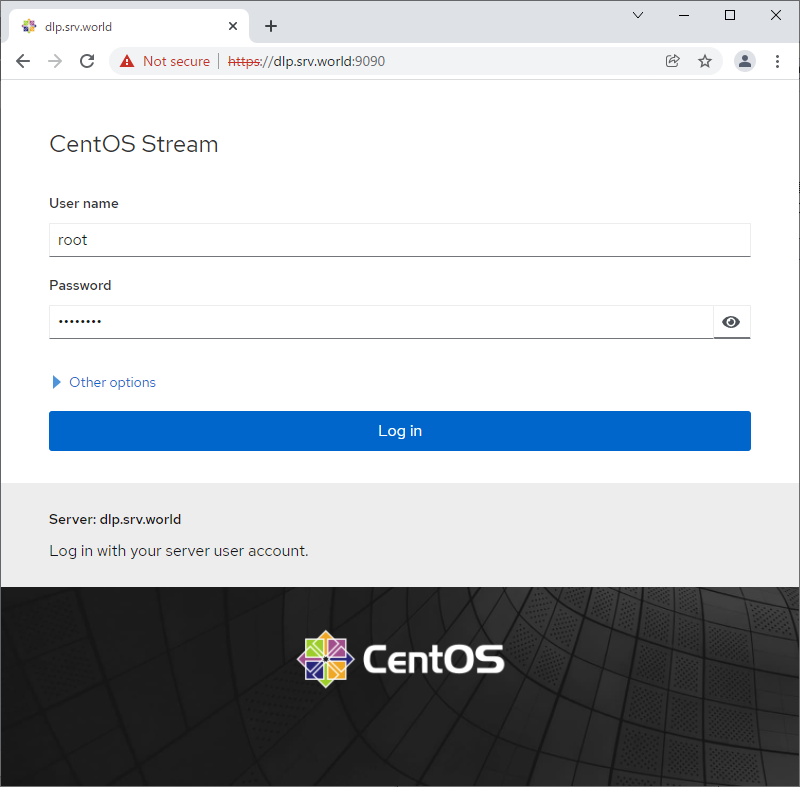
Step [2] Access to [https://(server's hostname or IP address):9090/] with Web browser from localhost or other Client compuers, then Cockpit login form is displayed like follows. Login with a local user on your Server. (It uses root user on this example).
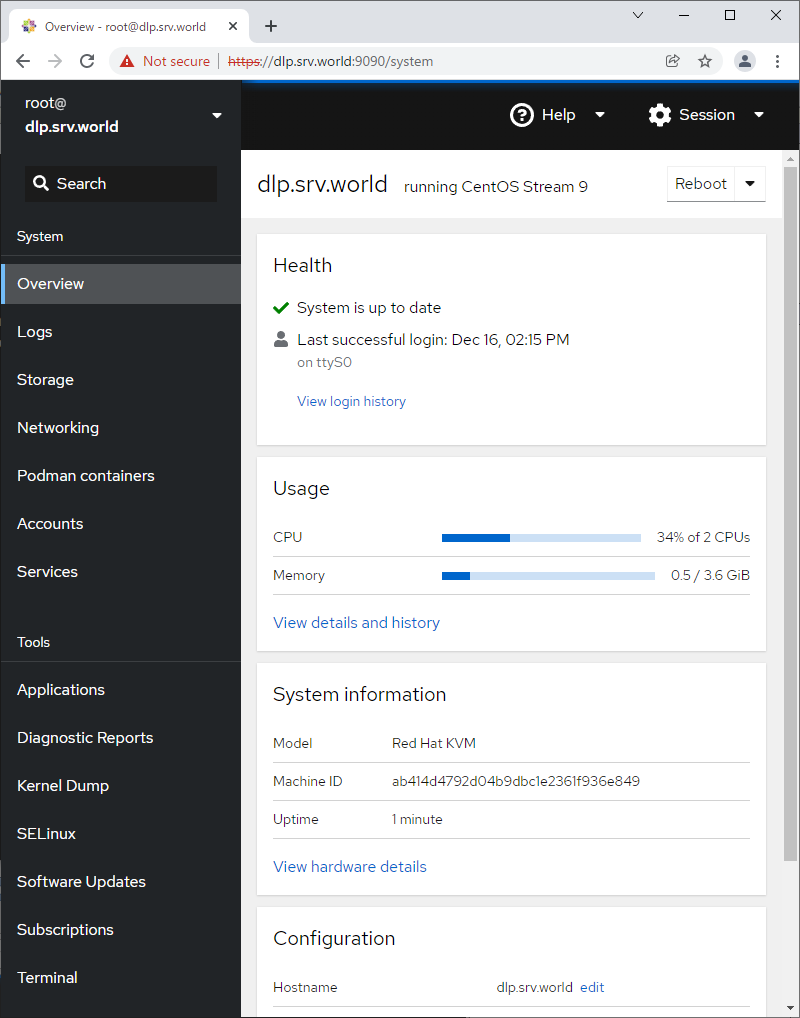
Step [3] This is the Cockpit index page. It's possible to manage various system settings on here.
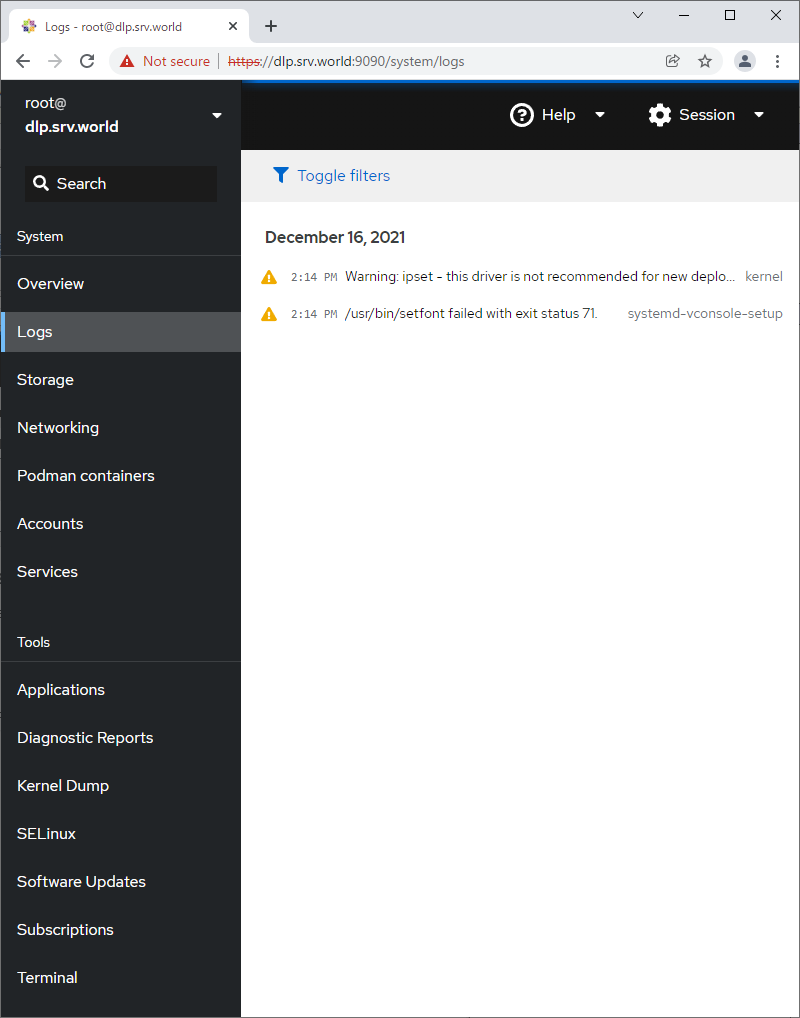
Step [4] For [Logs] on the left pane, it's possible to manage or operate [Journal] service that is the log management tool.
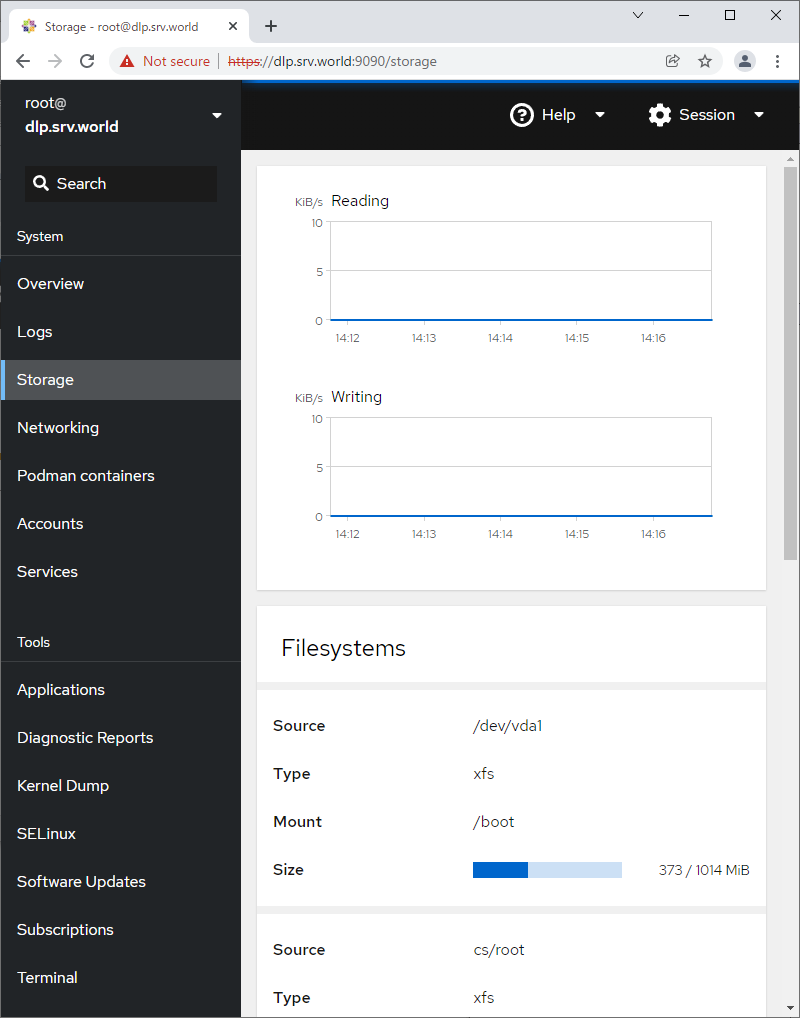
Step [5] For [Storage] on the left pane, it's possible to manage or operate Storages.
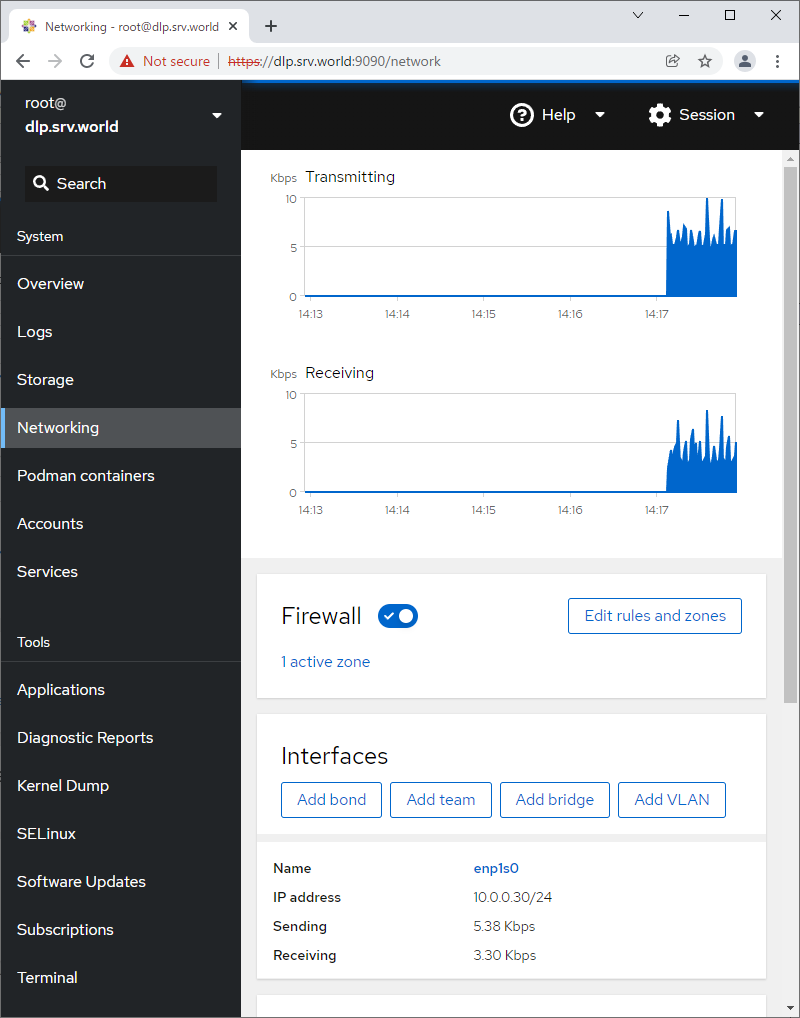
Step [6] For [Networking] on the left pane, it's possible to manage or operate Network settings.
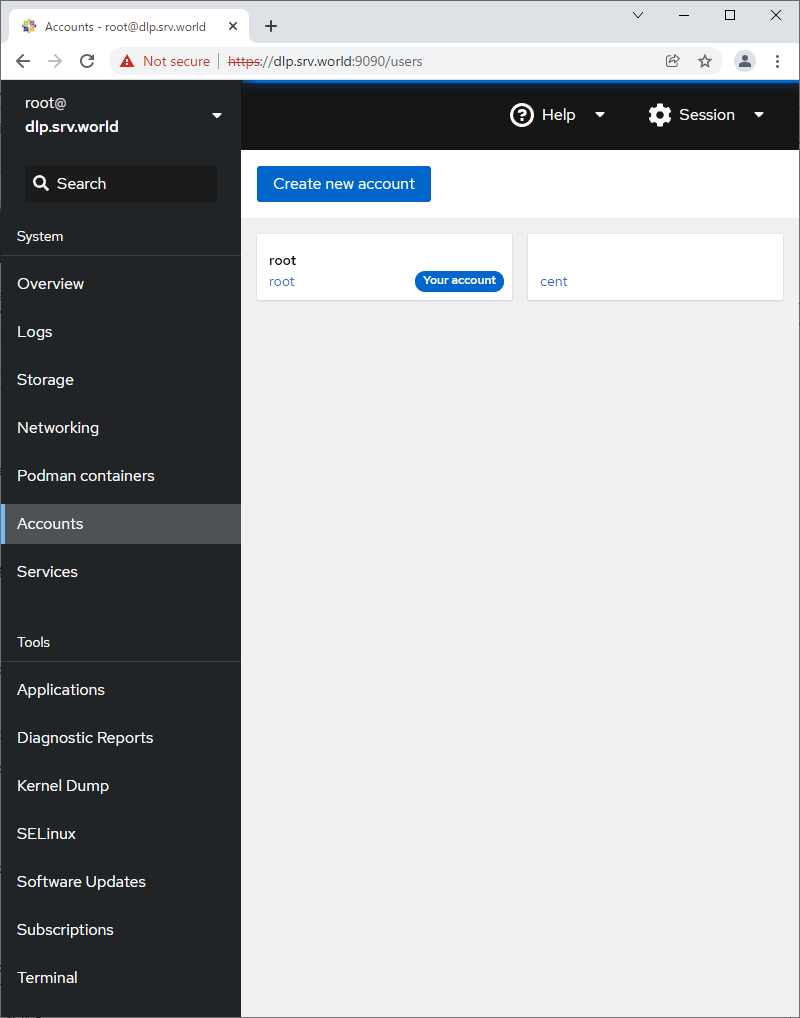
Step [7] For [Accounts] on the left pane, it's possible to manage or operate system accounts.
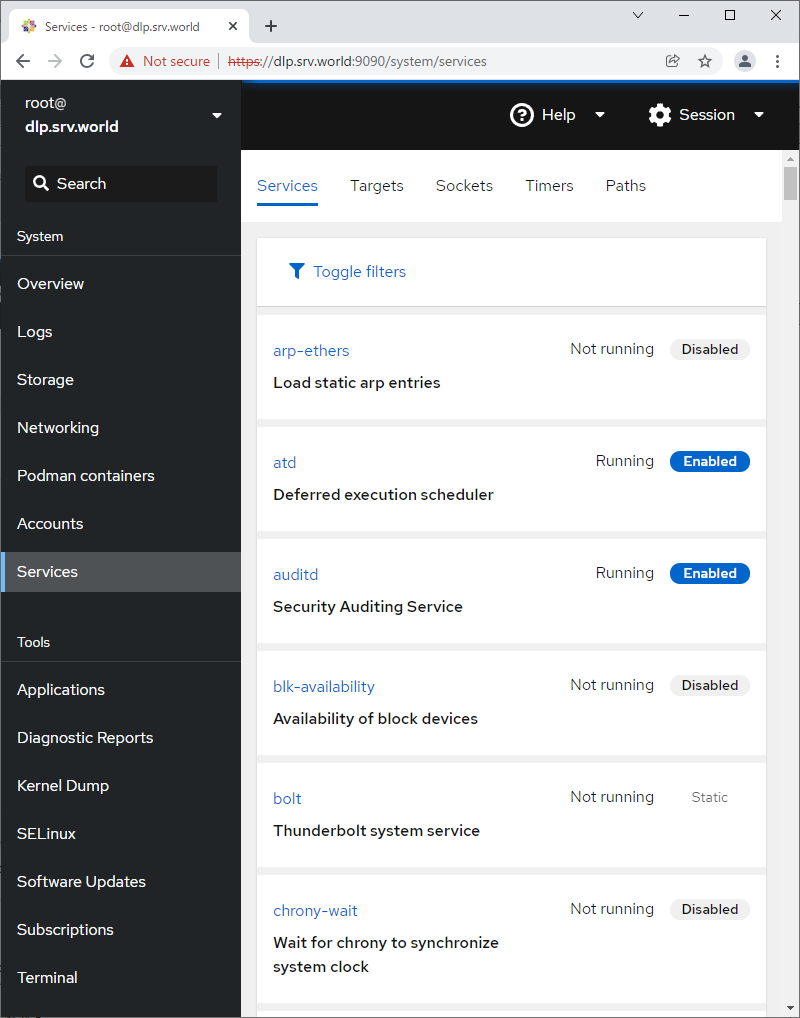
Step [8] For [Services] on the left pane, it's possible to manage or operate system services.
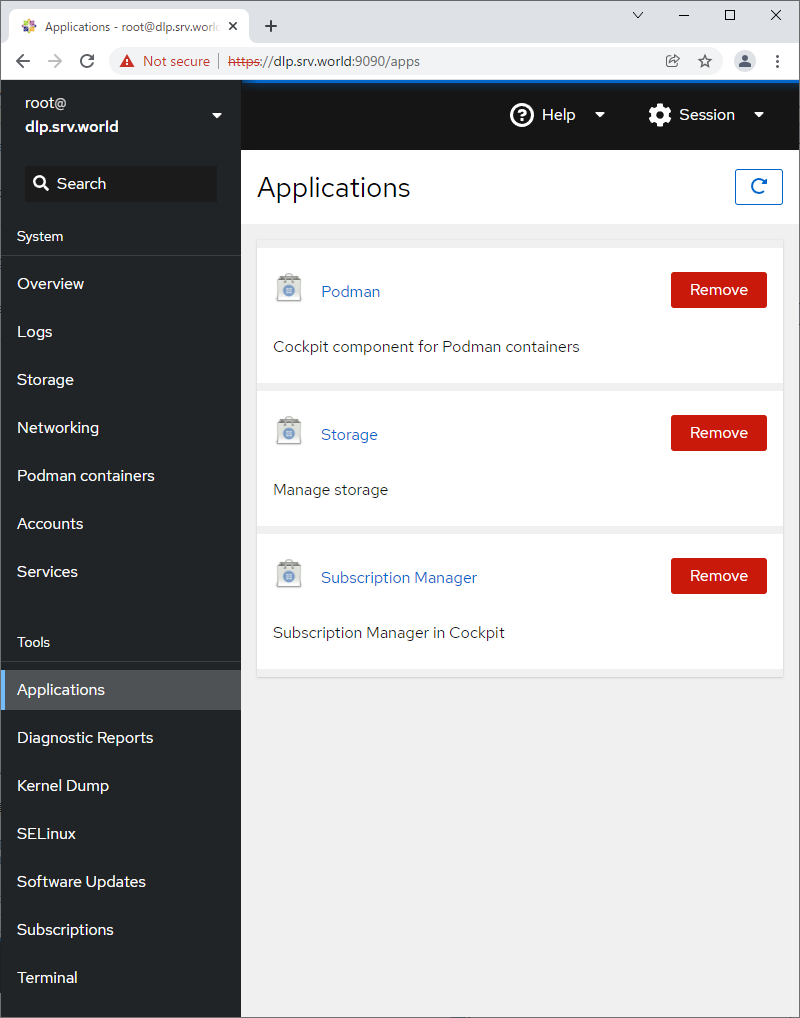
Step [9] For [Applications] on the left pane, it's possible to install or remove applications.
Step [10] For [Diagnostic Reports] on the left pane, it's possible to create or display System Diagnostic Reports.
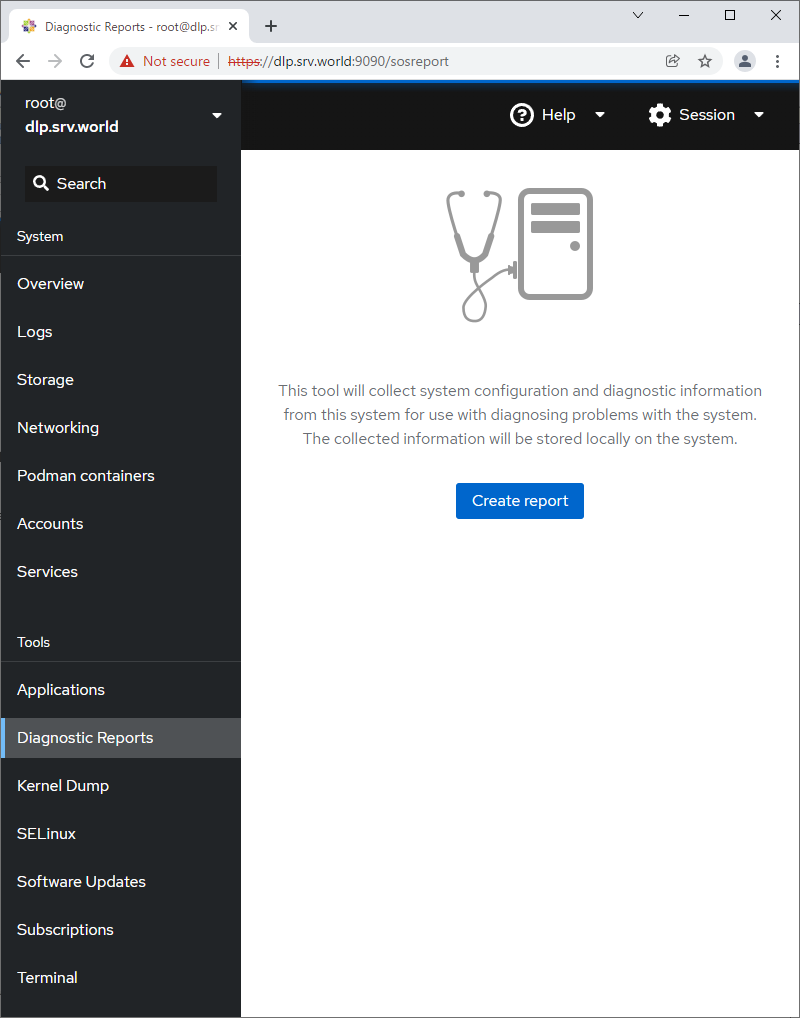
Step [11] For [Kernel Dump] on the left pane, it's possible to display Kernel Dump status. (based on [kdump] service is running state).
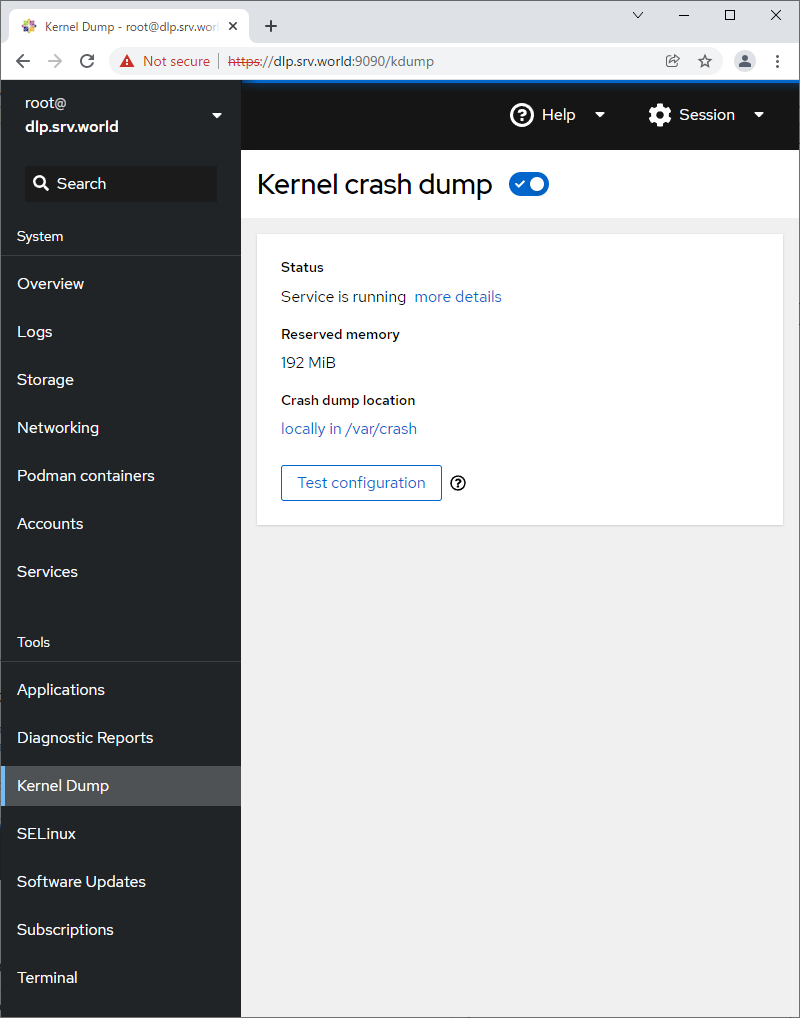
Step [12] For [SELinux] on the left pane, it's possible to display SELinux alert logs. (based on SELinux enabled state).
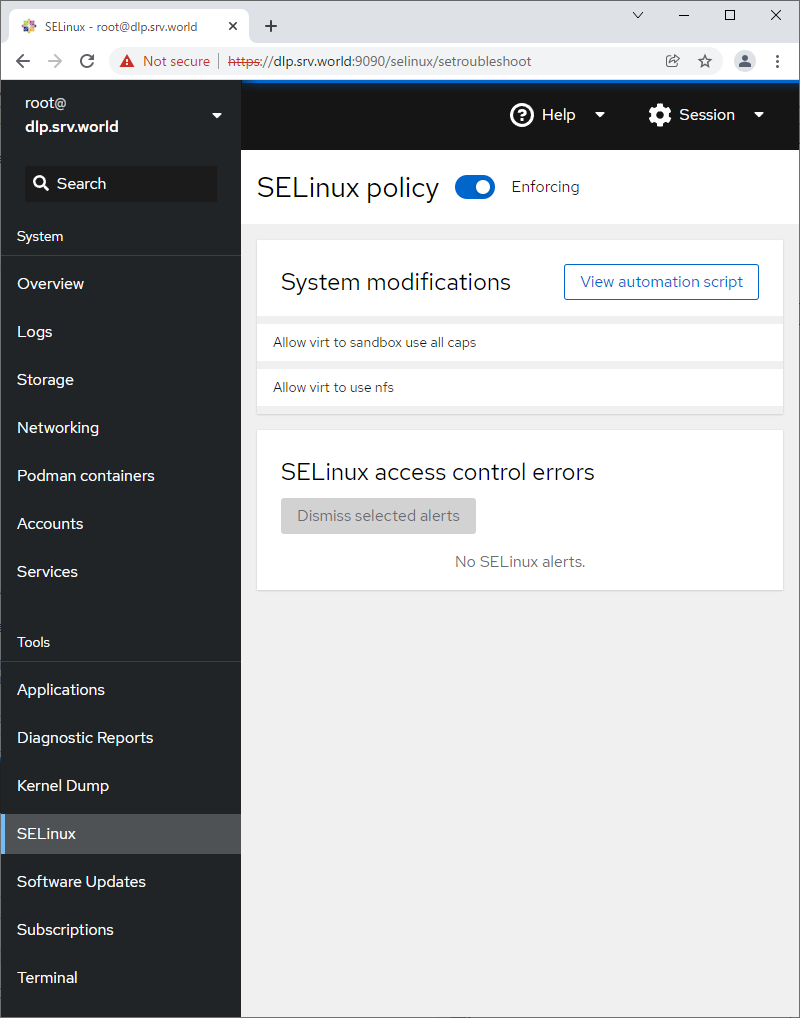
Step [13] For [Software Updates] on the left pane, it's possible to confirm updates or run update packages.
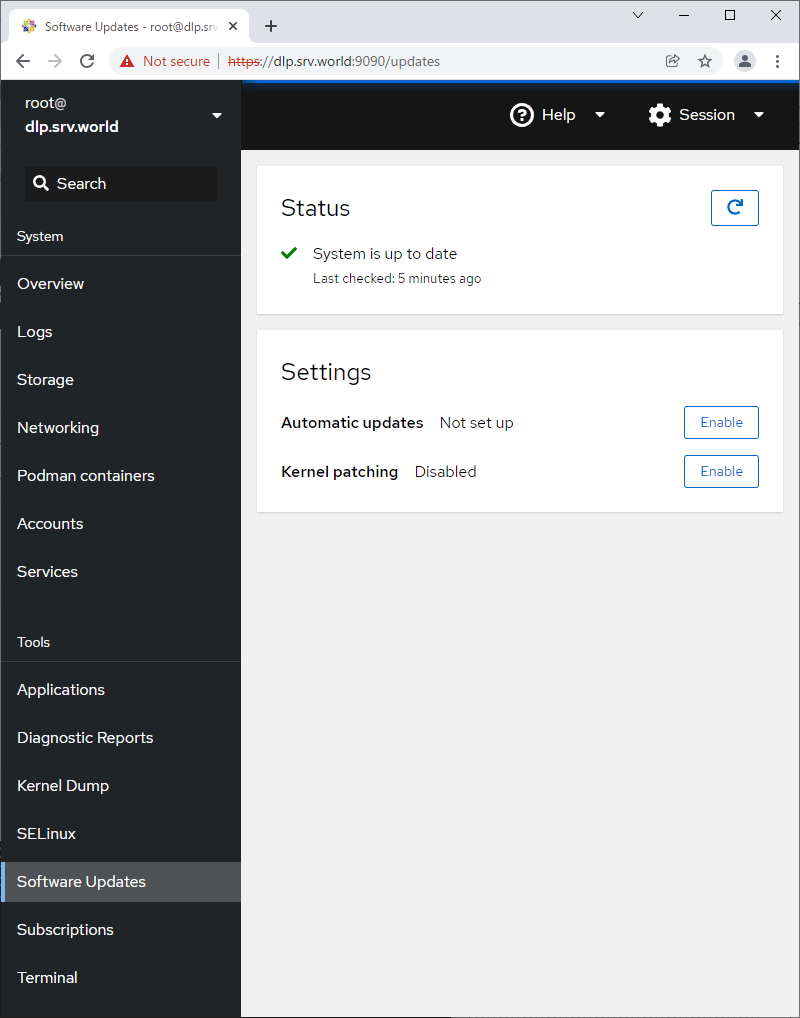
Step [14] For [Terminal] on the left pane, it's possible to operate system with commands directly.








Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for your comment! We appreciate your feedback, feel free to check out more of our articles.
Best regards, Bizantum Blog Team.